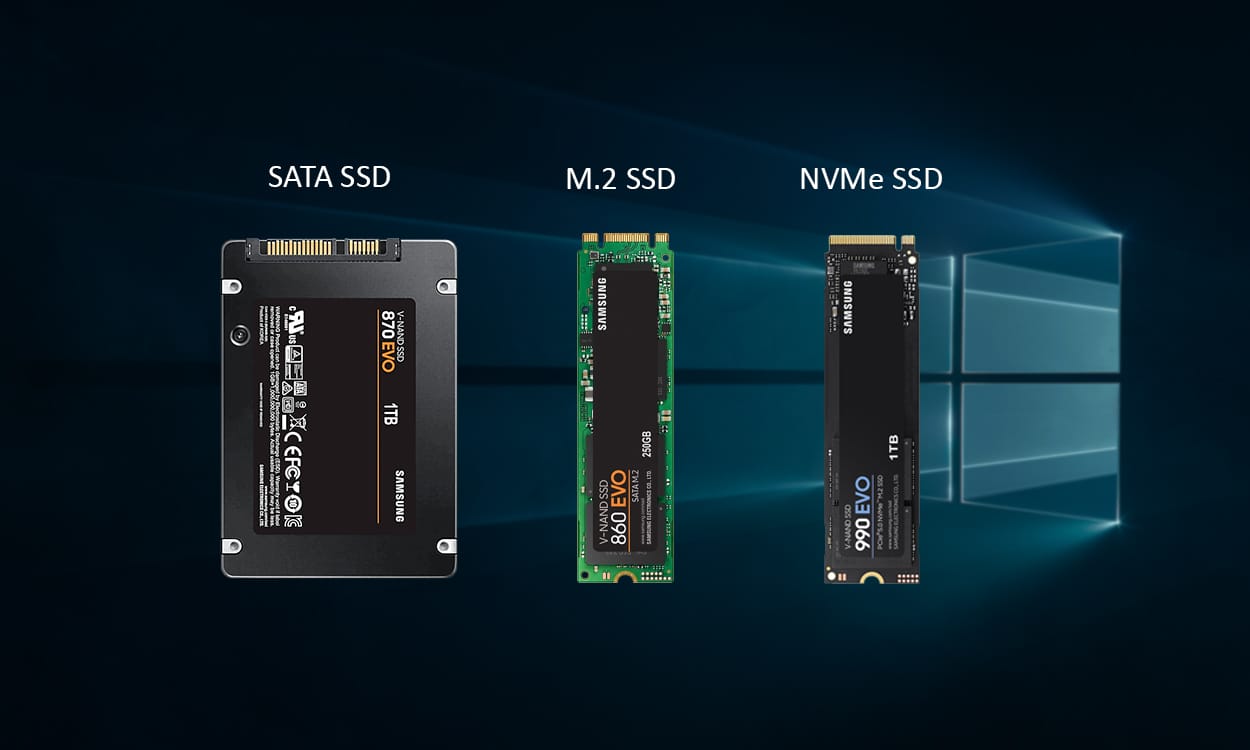
SSDs, M.2, and NVMe are all related to solid-state drives (SSDs) but differ in interface, size, and performance. Let’s Compare SSD vs M.2 vs NVMe in ultra mode. How many of you know NVMe drives can reach speeds of 4.0 GB/s? This is almost seven times faster than SATA SSDs. This huge speed difference is changing how we store data, making it important to know about modern SSDs.
In 2024, storage drives are changing fast. Data storage has greatly changed from old hard disk drives to quick NVMe SSDs. This guide will help you understand SSDs, M.2, and NVMe drives and choose the right storage for your needs.
Knowing the difference is key if you want to make your system faster or handle big data transfers. We’ll examine their shapes, speeds, and prices to give you a full view of today’s storage drive world.
Key Takeaways: Compare SSD vs M.2 vs NVMe
- NVMe drives offer significantly faster data transfer speeds than SATA SSDs
- M.2 is a form factor, not a performance indicator
- SATA SSDs are more budget-friendly but slower than NVMe options
- Storage capacities vary widely, with SATA drives offering up to 16TB
- NVMe drives can dramatically improve system start-up and gaming load times
Understanding Storage Drive Technologies
Storage drive technology has evolved greatly since the days of hard disk drives (HDDs). Solid-state drives (SSDs) now lead the market with better performance and reliability. Let’s examine how storage drives have changed and what makes SSDs effective.
What is Solid State Drive (SSD)
An SSD uses NAND flash memory to store data. Unlike HDDs, SSDs don’t have moving parts. This makes them faster at accessing and moving data. SSD technology has changed the game, offering much better performance than HDDs.
Evolution from HDD to Modern Storage
The move from HDDs to SSDs is a big step forward in storage tech. In 2011, NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) was introduced. Its ability to handle many commands simultaneously makes it faster than SATA and SAS protocols.
Basic Compare SSD vs M.2 vs NVMe: Components and Architecture
NAND flash memory is at the heart of SSD technology. It comprises an SSD’s basic structure, controller, and cache. The controller manages data flow, ensuring SSDs work well and last long.
| Interface | Max Speed | Queues |
|---|---|---|
| SATA M.2 | 6 Gbps | 1 |
| NVMe M.2 | 20 Gbps | 64K |
| PCIe Gen4 | 32 GB/s | 64K |
SSDs are much faster than HDDs. NVMe SSDs can be up to 25 times quicker than SATA SSDs. This big speed boost has made SSDs the top choice for everyone.
Compare SSD vs M.2 vs NVMe: Core Differences
When considering SSD types, it’s key to understand the differences between SATA SSDs, M.2 drives, and NVMe storage. Each has its own benefits in speed, size, and compatibility.
SATA SSDs use the SATA interface, limiting their speed to 550 MB/s for reading and writing. This is faster than old hard drives but slower than newer tech.
M.2 drives are a big step up in design. They can use SATA or NVMe, making them versatile and small. M.2 NVMe SSDs are fast and perfect for laptops and small desktops.
NVMe drives use PCIe lanes for super-fast data transfer. Gen 3 NVMe SSDs can write up to 3500 MB/s. Gen 4 models go even faster, up to 7000 MB/s. This makes NVMe drives much faster than SATA SSDs and HDDs.
| Drive Type | Interface | Max Read/Write Speed | Form Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| SATA SSD | SATA III | ~550 MB/s | 2.5″ or M.2 |
| NVMe Gen 3 | PCIe 3.0 | ~3500 MB/s | M.2 or Add-in Card |
| NVMe Gen 4 | PCIe 4.0 | ~7000 MB/s | M.2 or Add-in Card |
NVMe drives are the best choice for tasks like gaming or video editing. They handle lots of data at once. If you don’t need super speed, SATA SSDs are a good, affordable choice for everyday use.
Form Factors and Physical Specifications
SSD form factors have evolved to meet diverse storage needs. The 2.5-inch SATA SSD, once the standard, is now joined by more compact and efficient designs. Let’s explore the physical characteristics of different SSD types.
2.5-inch SATA SSD Design
The 2.5-inch SATA SSD looks like a traditional laptop hard drive. It measures 100mm x 70mm x 7mm and fits easily into most laptops and desktops. While still common, newer, more compact options gradually replace this form factor.
M.2 Form Factor Explained
M.2 sizes have become increasingly popular, especially in slim laptops. These stick-like SSDs come in various lengths, with 2280 (80mm long) being the most common. Other M.2 sizes include:
- 2242 (42mm long)
- 2260 (60mm long)
- 22110 (110mm long)
The versatility of M.2 sizes allows for flexibility in device design and storage capacity.
NVMe Physical Characteristics
NVMe SSDs typically use the M.2 form factor but can also be found in add-in card formats for PCIe slots. High-performance NVMe drives often include heatsinks to manage thermal output, ensuring optimal performance under heavy loads.
| Form Factor | Dimensions | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5-inch SATA | 100mm x 70mm x 7mm | Laptops, Desktops |
| M.2 2280 | 22mm x 80mm | Ultrabooks, Desktop Motherboards |
| PCIe Add-in Card | Varies | High-performance Desktops, Servers |
As technology advances, newer form factors like U.2 and EDSFF (Enterprise and Datacenter SSD Form Factor) are emerging. They offer improved performance and capacity for enterprise applications. The choice of SSD form factor depends on your specific needs, system compatibility, and performance requirements.
Performance Metrics and Speed Comparison
Speed is key when it comes to storage drives. Let’s explore how different technologies compare in SSD speed.
Read/Write Speeds Analysis
Storage drive speeds have greatly improved over time. Modern SATA SSDs can transfer data at up to 550MB/s. But, NVMe-based M.2 SSDs using PCIe Gen 4.0 can go much faster, reaching speeds over 7,500MB/s.
The latest PCIe 5.0 SSDs take it even further, with speeds hitting 14,500MB/s.
Data Transfer Capabilities
NVMe drives are much faster than SATA drives in data transfer. Some top NVMe models can read up to 6,900 MB/s and write at 4,100 MB/s. NVMe has direct CPU access and can handle multiple tasks simultaneously.
Real-world Performance Tests
In real life, NVMe SSDs are a big win for gaming and video editing tasks. They are five to ten times faster than SATA SSDs, which means big improvements in system response time and load time.
| Drive Type | Read Speed (MB/s) | Write Speed (MB/s) | Random Read IOPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| SATA SSD | 550 | 520 | 100,000 |
| NVMe PCIe 3.0 | 3,500 | 3,300 | 300,000 |
| NVMe PCIe 4.0 | 7,500 | 7,000 | 500,000 |
| NVMe PCIe 5.0 | 14,500 | 14,000 | 700,000 |
While the numbers are impressive, the difference between high-end SATA and NVMe drives might not be as big for everyday tasks. Your choice should depend on your specific needs and budget.
Interface Technologies and Connectivity
Storage drive interfaces are key to how fast data moves and how well a system works. SATA, introduced in 2003, is common in both HDDs and SSDs. SATA SSDs can reach 6 Gbps, but real speeds are about 550MB/s.
NVMe protocol is made for SSDs and talks directly to the CPU through PCIe lanes. This makes NVMe SSDs much faster, up to 20 Gbps. The best NVMe drives can exceed 3000 MB/s, and the newest ones can hit 7500 MB/s.
PCIe keeps getting better, offering more bandwidth with each update. Gen3 PCIe is 8 GT/s per lane, and Gen4 is 16 GT/s. Gen4 can handle 2 GB/s per lane, making things much faster.
| Interface | Max Speed | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| SATA III | 600 MB/s | General-purpose storage |
| PCIe 3.0 (NVMe) | 3500 MB/s | High-performance computing |
| PCIe 4.0 (NVMe) | 7500 MB/s | Professional workstations |
| PCIe 5.0 (NVMe) | 14500 MB/s | Cutting-edge applications |
The M.2 form factor supports SATA and PCIe, making it great for thin laptops and tablets. Knowing the difference between NVMe and SATA SSDs is important. It helps you choose the right one for your system’s needs.
Price-Performance Analysis CompareSSD vs M.2 vs NVMe
When looking at SSD prices, it’s key to think about value. We’ll dive into the cost-effectiveness and storage value of various options. This will help you choose wisely.

Cost per Gigabyte Comparison
SATA SSDs are more affordable, costing between $0.10 and $0.20 per GB. NVMe SSDs, though pricier at $0.20 to $0.40 per GB, offer better performance. High-capacity NVMe drives (8TB+) are more expensive but give unmatched speed and storage.
| Drive Type | Capacity | Price | Cost per GB |
|---|---|---|---|
| SATA SSD | 1TB | $80-$120 | $0.08-$0.12 |
| NVMe SSD (Gen4) | 1TB | $120-$200 | $0.12-$0.20 |
| NVMe SSD (Gen5) | 2TB | $240-$430 | $0.12-$0.22 |
Value Proposition for Different Uses
SATA SSDs are great for everyday use because they’re affordable and have plenty of storage. NVMe drives are best for tasks that need fast storage, like video editing or gaming. The Crucial P3, at $61.99 for 1TB, is a good choice for those watching their budget.
Market Price Trends
SSD prices are falling, making SATA and NVMe more comparable. For example, the WD Black SN850X 2TB NVMe Gen4 SSD now costs $124.99, down from $189.99. This makes high-performance storage more affordable for more people.
Compatibility and System Requirements
When you upgrade your storage, knowing about SSD compatibility and system needs is key. Your motherboard support is crucial in deciding which drives you can use. Let’s look at the basics for a smooth upgrade.
Motherboard Support
Your motherboard’s features affect SSD compatibility. SATA SSDs are compatible with most systems. For NVMe drives, you need a motherboard with M.2 or PCIe slots. Check your motherboard manual for support of these faster drives.
Operating System Considerations
Modern systems like Windows 10, macOS, and Linux support NVMe drives. Older systems might need BIOS updates or extra drivers for NVMe support. Always check your OS compatibility before buying a new SSD.
Installation Requirements
Installing an SSD requires matching its physical specs to your system. M.2 SSDs must fit your motherboard’s slot. PCIe 4.0 and 5.0 NVMe drives work with PCIe 3.0 slots but run slower. Make sure you have the right cables and brackets for 2.5-inch SATA SSDs.
| SSD Type | Motherboard Requirement | OS Support | Installation Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| SATA SSD | SATA port | Universal | Needs SATA cable and power |
| M.2 SATA | M.2 slot (B-key) | Universal | Direct motherboard insert |
| M.2 NVMe | M.2 slot (M-key) | Windows 10+, recent macOS/Linux | May need BIOS update |
| PCIe NVMe | PCIe slot | Windows 10+, recent macOS/Linux | Requires add-in card |
Use Case Scenarios and Applications
SSD applications are diverse and offer benefits in many areas. SATA SSDs are great for everyday tasks like office work. They make computers faster, allowing files and programs to open quickly.
NVMe SSDs stand out in specific tasks. For example, they help content creators with 4K video and 3D rendering. These drives cut down on time, making work more efficient.
Gamers also see big gains with NVMe SSDs. They need fast loading and smooth graphics. NVMe drives help with this, making games run better.
NVMe SSDs boost server database performance. They handle many tasks simultaneously, speeding up data access and improving servers.
Laptop users find M.2 NVMe SSDs perfect. They offer fast speeds and save battery life. This means laptops last longer on a charge.
| SSD Type | Best Use Cases | Performance Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| SATA SSD | General computing, Office work | Improved system responsiveness |
| NVMe SSD | 4K video editing, 3D rendering, Competitive gaming | Faster rendering, Reduced load times |
| M.2 NVMe SSD | Laptops, Ultrabooks | High performance, Energy efficiency |
Future of Storage Technology
The world of storage technology is changing fast, and exciting advancements are coming. PCIe Gen 5.0 and beyond will change how we transfer data and perform tasks.
PCIe Gen 5.0 and Beyond
PCIe Gen 5.0 in NVMe drives will bring faster speeds and less delay. This new standard will support bigger drives and might be faster than PCIe Gen 4. PCIe Gen 6.0 and 7.0 are also in the works, with the intention of improving storage performance even more.
Emerging Storage Solutions
New SSD technology is all about speed, power use, and keeping data safe. Industrial-grade SSDs can handle tough conditions, keeping data safe. The EDSFF (Enterprise and Datacenter SSD Form Factor) is becoming popular, with sizes like E1.S and E1.L for more storage in data centres.
Industry Trends
The industry is moving towards bigger storage, faster speeds, and better endurance. NVMe SSDs are leading the way, offering up to 25 times faster than SATA. They can handle up to 64K I/O queues, making data processing more efficient in the future.
FAQ
What’s the main difference between SATA SSDs, M.2 SSDs, and NVMe SSDs?
SATA SSDs are 2.5 inches in size and use SATA, reaching speeds of 550 MB/s. M.2 SSDs are smaller, with speeds depending on the interface. NVMe SSDs are the fastest, reaching up to 7,500 MB/s with PCIe Gen 4.0.
Are NVMe SSDs always faster than SATA SSDs?
Yes, NVMe SSDs are faster. They can read and write data over 7,500 MB/s, while SATA SSDs top out at about 550 MB/s. But for everyday tasks, the difference might not be huge.
Can I use an NVMe SSD on any computer?
Not all computers support NVMe SSDs. Your system must have a compatible motherboard. Most modern systems (post-2015) support NVMe. Check your motherboard specs or computer manual.
What’s the price difference between SATA and NVMe SSDs?
NVMe SSDs cost more, between $0.20 to $0.40 per GB. SATA SSDs are cheaper, from $0.10 to $0.20 per GB. Prices are dropping, making the difference smaller.
Are M.2 SSDs always NVMe?
No, M.2 SSDs can support SATA or NVMe. Some M.2 SSDs are similar to 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, while others use the faster NVMe protocol.
What tasks benefit most from NVMe SSDs?
NVMe SSDs are best for fast data access tasks, such as 4K video editing, 3D rendering, and gaming. They’re also great for professionals working with large files.
How do I know if my laptop can be upgraded with an M.2 or NVMe SSD?
Check your laptop’s specs or manual for M.2 slots. Use system tools or inspect your laptop for M.2 slots. Make sure it supports SATA, NVMe, or both.
What’s the future of SSD technology?
SSDs will get faster with new PCIe standards. They’ll also have higher capacities and lower latencies. New technologies like 3D XPoint memory are coming. The focus is on speed, power efficiency, and security.
Do NVMe SSDs require special cooling?
Not all NVMe SSDs need special cooling, but high-performance models might. Some come with heatsinks; others might need extra cooling, especially in small or high-performance systems.
Can I use a PCIe 4.0 NVMe SSD in a PCIe 3.0 slot?
PCIe 4.0 NVMe SSDs work in PCIe 3.0 slots and run at PCIe 3.0 speeds. This is still faster than SATA SSDs but slower than PCIe 4.0.