One in five adults has type 1 high blood pressure. Many people don’t even realize they have high blood pressure in early age, often known as hypertension, because it has no symptoms or early warning signals. However, the damage to your arteries, kidneys, and heart is exponentially accelerated when high blood pressure is accompanied by excessive cholesterol and blood sugar levels.

A healthy lifestyle at a young age and well-controlled habits are the cornerstones of managing high blood pressure in the early age of 40 and under, whether or not you require medication. A balanced lifestyle approach to management also helps people feel more in control of their good health.
Normal blood pressure is defined as a reading of less than 120/80 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). Elevated pressure means systolic blood pressure (the first number in a reading) is 120 to 129 mm Hg, with a diastolic pressure (the second number) of less than 80 mm Hg. People who have consistent readings of 130 to 139 for systolic pressure or 80 to 89 for diastolic pressure are said to have high blood pressure (stage 1 hypertension).

Taking medication to lower high blood pressure is a proven way to reduce your risk for heart disease. However, adopting lifestyle changes may let you maintain healthy lives and perhaps even avoid permanent drug therapy.
Sometimes, people are reluctant to start a drug because they don’t want to be dependent on medication, which may lead to increased damage or chronic inflammation. Science has proven that chronic, low-grade inflammation can turn into a silent killer that contributes to cardiovascular disease, cancer, type 2 diabetes, and other organ conditions. Easy natural ways to lower blood pressure and make lifestyle changes can be as effective as the best medication.

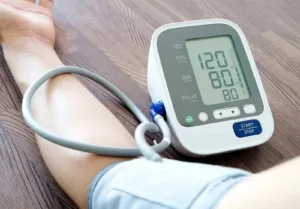
Dr. Howard LeWine, Editor-in-Chief of Harvard Men’s Health Watch. “For people with elevated blood pressure or stage 1 hypertension, the first order of business is to get serious about modifying their lifestyle.”
Following easy, natural ways to manage high blood pressure at an early age without medicine:
1, Sound Sleep Benefits:

Getting enough good sleep has a lot of proven health benefits. Adults (18+ years) get 7-9 hours of sleep daily. Silent sleep can maximize problem-solving skills and enhance memory. Sleep is important for various aspects of brain function. Cognition, concentration, productivity, and performance are all negatively affected by a lack of sleep. Sleep is important for maintaining a healthy heart. Quality sleep promotes cardiac health. During sleep, the heart rate slows down, and blood pressure decreases. Sleep helps regulate blood sugar levels. Getting enough sleep can help lower stress levels.
2, Daily Exercise:

Guidelines call for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. A reasonable starting goal is 20 to 30 minutes every other day. Any kind of exercise is always better than nothing. But if you need motivation, join a walking club or sports league (like golf, bowling, basketball, or pickleball), hire a personal trainer, or sign up for fitness classes at a gym or community center. You can also increase your daily movements, like walking for five minutes every hour, doing two sets of five to 10 push-ups on the floor or against the kitchen counter, or doing 20 minutes of yoga or stretching.
3, Healthy Diet:

While most experts advocate plant-based diets to help lower blood pressure numbers, a recent study found that the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet may have the most significant impact. The researchers found that adopting the DASH diet could prevent an estimated 15,000 annual heart attacks and strokes among men with high blood pressure. DASH emphasizes fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, nuts, seeds, and grains, limiting consumption of red meat, sodium, and sugar-sweetened foods and drinks.
4, Obesity Management:

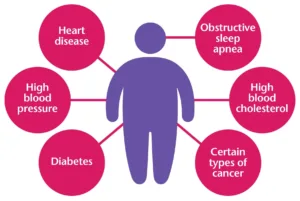
Body mass index measures body fat based on height and weight. Everyone has to use a BMI calculator to determine their BMI and see where they fall on the chart. A healthy BMI range is between 18.5 and 24.9. Weight gain at a young age is common and can be managed with good planning for a healthy lifestyle. BMI Calculator.
5, Alcohol Limit:


According to the “Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020-2025,” U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the U.S. Department of Agriculture, adults of legal drinking age can choose not to drink or to drink in moderation by limiting intake to 2 drinks or less in a day for men and 1 drink or less in a day for women when alcohol is consumed. Drinking less is better for your health than drinking more.
6, Sodium Level:

“People with high blood pressure in early age sometimes significantly improve by avoiding sodium,” says Dr. LeWine. Processed foods account for much of the sodium that people consume. These include foods like canned vegetables and soups, frozen dinners, lunch meats, instant and ready-to-eat cereals, salty chips, and other packaged snacks. Cut back on these items, or select low-sodium options.
7, Stress: Most Important to Control:

Stress can affect the heart and cardiovascular system in various ways. It can lead to high blood pressure, hypertension, heart rhythm problems, and artery damage. It can also cause inflammation in the arteries, plaque buildup, and increased blood sugar levels, which are risk factors for atherosclerosis and heart attack. Stress can also reduce blood flow to the heart, especially in people with heart disease, and increase the likelihood of unhealthy behaviors like smoking, drinking, overeating, and drug use. Managing stress may lower the risk of heart problems.
8. Blood pressure checkup:
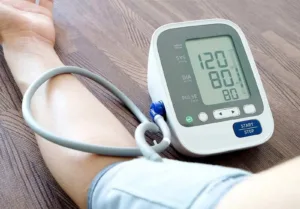
The normal level of blood pressure is under 40 years as The American Heart Association recommends that blood pressure should be less than 120/80 mm Hg. It is mandatory to check every 4-6 months or when required for people under 40 years old. Once a year get a full body profile blood test report to measure the parameters.
Conclusion to prevent High Blood pressure in early age:
- Eat a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats.
- Avoid sugary drinks and foods that are high in calories and low in nutrients.
- Avoid More alcohol and smoke first.
- Limit your intake of processed foods and fast food.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Get enough sleep each night.
- Exercise regularly. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
Remember that it’s important to maintain a healthy body without medicine throughout your life.



